CODESYS example: ModbusTCP-RTU-Slave
Introduction
In this example, we configure and run both a Modbus TCP slave and a Modbus RTU slave on the RevPi Connect+ with CODESYS Control for Linux ARM/ARM64. The application is designed to copy the first 10 holding registers to the 10 input registers of both slaves.
Prerequisites
Hardware Requirements
- RevPi Connect+
- One Modbus TCP slave
- One Modbus RTU slave
Software Requirements
- CODESYS Development System installed on your PC
Preparation
Hardware Setup:
Tipp: For detailed instructions about how to set up your system, refer to the Getting Started guide.
Software Setup:
note: To ensure a compatible system with suitable software, please refer the following links:
Overview
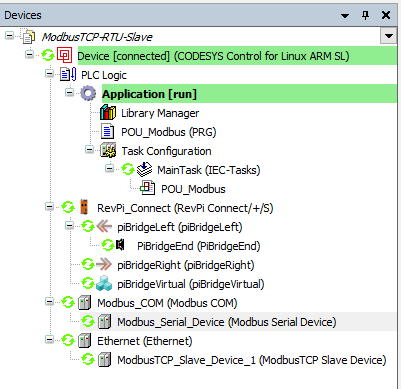
The following figure provides an overview of the CODESYS device tree for the setup:
Adapting for RevPi Core or Compact
To adapt the project for RevPi Core or RevPi Compact:
▷ Right-click on RevPi Connect in the CODESYS device tree.
▷ Select Update device.
▷ Choose RevPi Core or RevPi Compact as the replacement and rename the device accordingly.
Step 1: Configuring Modbus RTU Serial Port
For RevPi Connect or RevPi Core:
-
Edit the configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/CODESYSControl_User -
Add the following line:
[SysCom]
Linux.Devicefile=/dev/ttyUSB -
Map the COM ports in CODESYS as follows:
- /dev/ttyUSB0 → COM port 1
- /dev/ttyUSB1 → COM port 2
- /dev/ttyUSBn → COM port n
If an extra USB-485 converter is connected, the correct COM port has to be identified.
For RevPi Compact:
- Default RS485 Port:
▷ Edit/etc/CODESYSControl_Userand add:[SysCom]
Linux.Devicefile=/dev/ttyAMA - Using USB-485 Converter:
▷ Add the following line instead:[SysCom]
Linux.Devicefile=/dev/ttyUSB
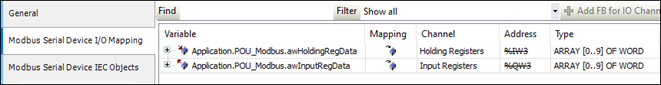
Step2: Configuring Modbus RTU Slave
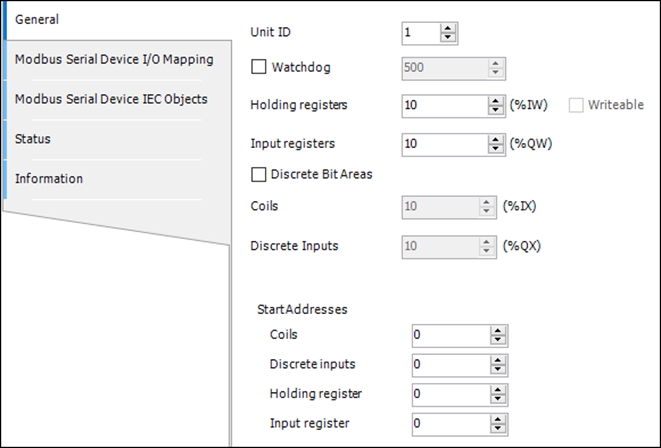
▷ Map Holding Registers and Input Registers to the application POU_Modbus to make the data accessible to the application logic.
Step 3: Configuring Modbus TCP Slave
The configuration for the Modbus TCP slave is similar to that for the Modbus RTU slave.
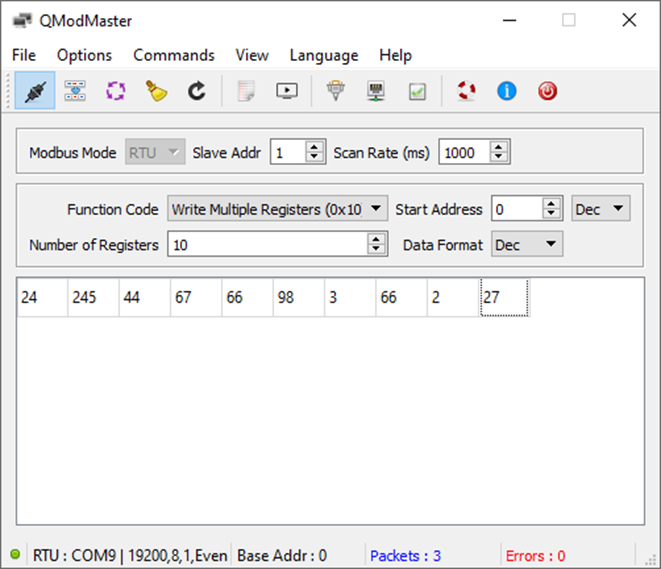
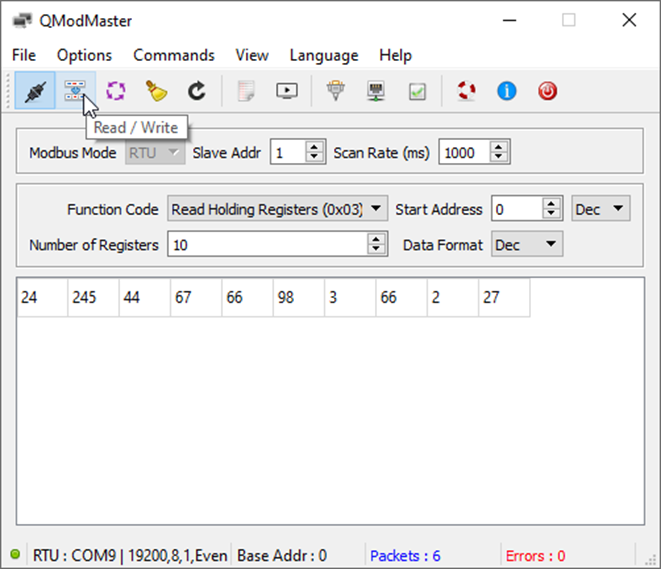
Step 4: Simulating Modbus TCP and RTU Masters
-
Required Software:
- Use the application QModMaster for simulation. You can download it here.
-
Functionality:
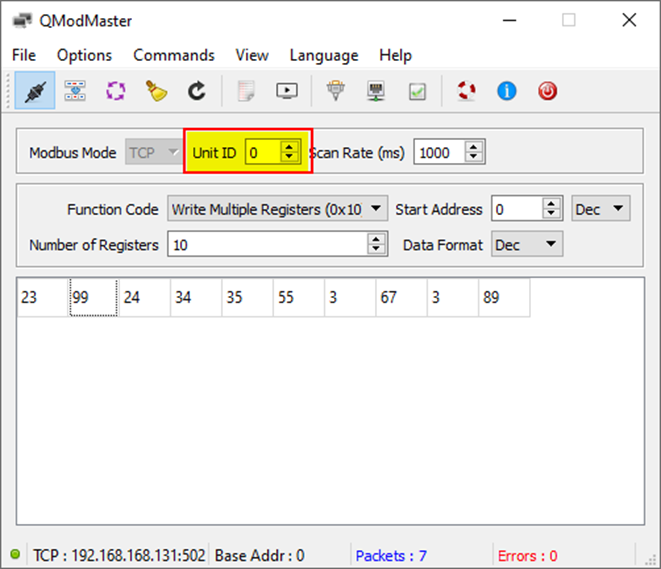
- Write Multiple Registers: Writes data to the holding registers of the slave.
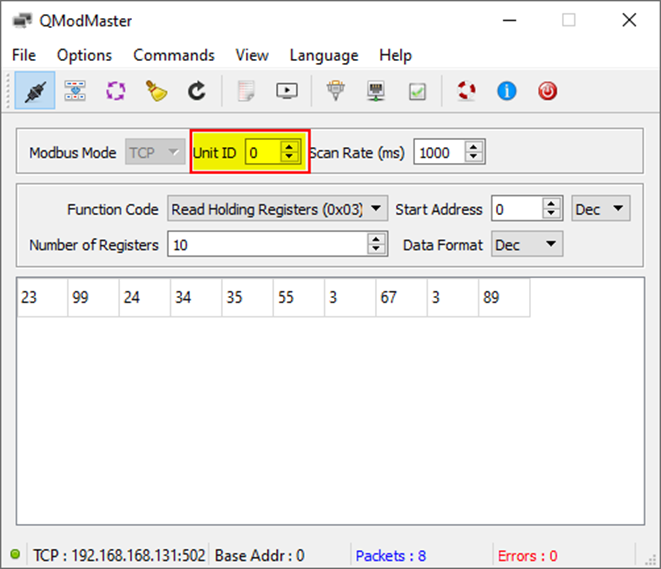
- Read Holding Registers: Reads back the input register data of the Modbus TCP/RTU slave running on the RevPi device.
Step 5: Modbus TCP Unit ID
- The Modbus TCP Unit ID serves the same function as the slave ID.
- The Unit ID
255is recommended for addressing the gateway itself. - When using QModMaster, note that it uses Unit ID
0instead of255for addressing the gateway.