RevPi Connect 4
Product Description
The RevPi Connect 4 is a robust 24 V industrial PC for IIoT and automation projects based on the Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4. The RevPi is a basic module from the Revolution Pi family. All devices in the Revolution Pi family are developed in accordance with EN 61131-2.
Components
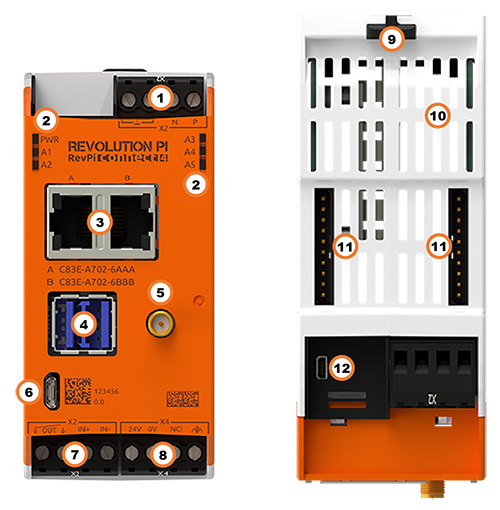

| Position | Component | Application |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | X2 connector RS485 | Serial Devices (RS485), Connecting the UPS |
| 2 | 6 × status LED | LEDs |
| 3 | 2 × RJ45 Ethernet | Ethernet Interfaces, Establishing a Network Connection |
| 4 | 2 × USB A 3.2 Gen 1 | USB Interfaces |
| 5 | RP-SMA socket1 | WLAN and BT |
| 6 | Micro USB | Saving and Reinstalling the Image |
| 7 | X2 connector | Relay output, Digital input |
| 8 | X4 connector | Connecting the Power Supply |
| 9 | 2 × locking clip | Mounting the Device on a DIN Rail |
| 10 | Ventilation Slots | Mounting the Device on a DIN Rail |
| 11 | 2 × PiBridge | Connecting Expansion Modules |
| 12 | Micro HDMI | Set up Desktop Mode |
1 only for the variants with WLAN
Compatible RevPi Image
- RevPi Bookworm Image
- RevPi Bullseye Image
See: RevPi Images.
Variants
| Item No.: | RAM | eMMC | WLAN |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100376 | 2 GB | 8 GB | No |
| 100377 | 2 GB | 8 GB | Yes |
| 100378 | 4 GB | 32 GB | No |
| 100379 | 4 GB | 32 GB | Yes |
| 100395 | 8 GB | 32 GB | No |
| 100380 | 8 GB | 32 GB | Yes |
For available variants see Revolution Pi Shop.
Extension Modules
The RevPi Connect 4 base module can be expanded by up to 10 expansion modules to create a Revolution Pi system:
| Left side | base module | Right side |
|---|---|---|
| 5 × RevPi I/O module | RevPi Connect 4 | 5 × RevPi I/O module |
Compatible I/O Modules
- RevPi DIO - Digital I/O expansion module
- RevPi DI - Digital input expansion module
- RevPi DO - Digital output expansion module
- RevPi AIO - Analog I/O expansion module
- RevPi MIO - Analog & digital I/O expansion module
- RevPi RO - Relay output expansion module
Virtual Devices
The Virtual Devices are delivered with the RevPi image as components in PiCtory included:
Scope of Delivery
The scope of delivery includes
- RevPi Connect 4(base module)
- X4 connector
- 2 × X2 connector
- 2 × cover plug for PiBridge
- Supplement
Mounting and Connecting
The RevPi was developed for use in a control cabinet. Observe the specifications for the Intended Use and all Safety Instructions. Intended UseSafety Instructions
Danger to life due to electric shock
There is a risk of fatal electric shock when working on devices in the switch cabinet with 230 V mains voltage.
▷ Work in the switch cabinet may only be carried out by qualified electricians.
▷ Before carrying out any work in the switch cabinet, switch off the power supply properly.
Carry out the installation and connection in the following order :
-
Mount the RevPi base module and all expansion modules on a DIN rail.
-
Connect the expansion module via the PiBridge connector.
-
Connect all other devices such as sensors and actuators. The interfaces available to you for this can be found in the Componentssection.
-
Connect a monitor and a keyboard if you want to operate the RevPi in desktop mode. This is not necessary if you can access the RevPi via a network connection.
-
As the last step connect the power supply.
Connecting the UPS
A UPS (uninterruptible power supply) ensures that devices continue to function during a fault. Depending on the type of UPS, a UPS can protect against the following faults:
- Power failure
- Overvoltage
- Undervoltage
- Frequency changes
- Harmonics
The RevPi has a digital input, to which the status output of a UPS can be connected.
▷ Please check whether your UPS is suitable for connection to the RevPi.
▷ Connect the status output of the UPS to the digital input on the X2 connector (pin IN and pin ⫠).
▷ Observe the installation specifications of the UPS manufacturer.
▷ Test the UPS.
In the process image, bit 6 of the RevPiStatus variable is 0 or 1, depending on whether 0V or 24V is applied to the input. Your application must read this bit cyclically. If the UPS reports a problem, your application must initiate a corresponding measure. What exactly should be done depends on:
- the size of the battery used,
- the current consumption of the RevPi,
- the current consumption of all components that are additionally connected to the UPS.
Typically, the system is brought into a safe state and the RevPi is shut down.
Access to the Device
The RevPi is accessed in two steps:
Install all available Updates as soon as the RevPi is connected to the internet, so that the system is always up to date with security-relevant features.
Alternatively, access is possible without a network, see Desktop Mode.
See also:
Configuration
Basic Configuration
From the RevPi Bookworm image (10/2024) onwards, the basic configuration of the RevPi devices is carried out via the Cockpit web application.
Until the RevPi Bullseye Image (04/2024), the basic configuration of the RevPi devices is carried out via the RevPi Status web application.
System Configuration
The Revolution Pi system, i.e. a RevPi base module with expansion modules, is configured via the PiCtory web application.
Configuring the Base Module in PiCtory
▷ Start PiCtory.
▷ Select the RevPi base module from the Device Catalog and drag and drop it onto the empty slot with position number 0.
❯ The configurable values appear in the Value Editor.
▷ Save the configuration as the start configuration with File > Safe as Start-Config.
❯❯ The start configuration is called up directly after each boot process.
| Value | Function |
|---|---|
| INP RevPiStatus | Status of the piControl driver |
| INP RevPiIOCycle | Cycle time of piBridge communication between base module and expansion modules in ms |
| INP RS485ErrorCnt | Error counter for piBridge communication |
| INP Core_Temperature | CPU Temperature |
| INP Core_Frequency | CPU Frequency |
| OUT RevPiOutput | Output value for relay contact |
| OUT RS485ErrorLimit1 | First limit value for error counter > Message in kern.log |
| OUT RS485ErrorLimit2 | Second limit value for error counter > piBridge communication is stopped |
| OUT RevPiLED | Status byte for LEDs |
Serial Devices (RS485)
The RevPi has an RS485 interface on the upper X2 connector to connect serial devices such as sensors.
The socket has differential data line terminals P/N and reference terminals (internal GND and functional earth via 1 MOhm RC network).
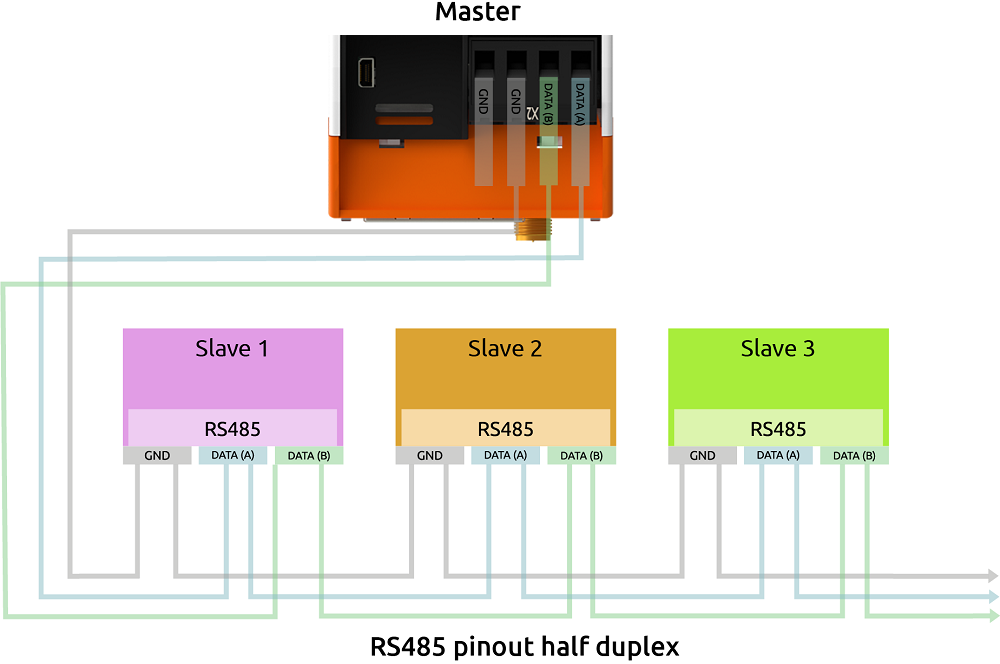
Under Linux, the interface can be addressed via the device driver node with :
/dev/ttyRS485
How you use this connection optimally depends on your project environment. The network you are working with or the EMC load are individual factors that influence how you assign this connector.
We are therefore unable to show you an optimal solution for your individual project, but we have compiled a list of the problems that can occur and tips on how you can solve them.
RS485 is a fully differential line and does not normally require a third GND line. However, due to the limits of the input receivers ("maximum common mode voltage"), there may be problems with the signal quality if no potential reference is used between the transmitter and receiver. However, connecting the internal GND to a line that is subject to EMC can lead to EMC problems within the RevPi Connect.
We therefore recommend that you use a common functional earth between all RS485 network participants. This gives you a good, common reference potential for the differential bus signal.
If this does not work either, you can connect the FE terminal of the RS485 connector to the third (GND) line of the bus.
You can also try to solve signal problems with the GND terminal.
Ethernet Interfaces
The RevPi can be connected to a network via the RJ45 interface.
Two 10/100 Ethernet connections are available on the RevPi, which are independent of each other. This allows the RevPi to be integrated into two different networks. The MAC addresses are printed on the front of the housing.
Under Linux, the interfaces can be addressed with:
- Socket A:
eth0 - Socket B:
eth1
WLAN and BT
Prerequisites
✓ RevPi base module with WLAN interface
✓ DHCP-capable WLAN router
✓ Optional: external RP-SMA WLAN antenna
The WLAN interface operates at 2.4 and 5 GHz and complies with the IEEE802.11a/b/g/n/ac specification.
Under Linux, you can address the WLAN interface with , provided no other WLAN devices are used:
wlan0
Activate WLAN via RevPi status
▷ Start RevPi Status.
▷ Activate the Enable/Disable build-in WLAN option in the CONFIG tab.
Set up WLAN country code via raspi-config
The regulations and frequency ranges for WLAN networks are different for each country. Configure the WLAN country code so that the RevPi does not transmit in prohibited areas or cause interference.
▷ Log in to the RevPi via a terminal.
▷ Open raspi-config with the command:sudo raspi-config
▷ Use the arrow keys to navigate to the Localization Optionsmenu.
▷ Select the WLAN Countryoption.
▷ Select the appropriate country from the country list and confirm with ENTER.
❯❯ The WLAN country code is active.
Set up WLAN connection via NetworkManager
The WLAN connection is set up via the NetworkManager nmtui. The NetworkManager is a terminal-based user interface for managing network connections under Linux.
▷ Log in to the RevPi via a terminal.
▷ Start nmtui with the commandsudo nmtui
❯❯ The nmtui user interface appears.
Use the arrow and ENTER buttons to navigate within nmtui.
▷ Select Edit a connection.
▷ Select the appropriate Wi-Fi network.
▷ Enter the WLAN password under Password and configure any other WLAN settings.
▷ Save the settings with OK and return to the home screen with *Back *.
▷ Select Activate a connection.
▷ Select the Wi-Fi network and activate the connection with the ENTER button.
❯ The status message Connecting ... appears.
❯ The WLAN connection is established.
Setting up BT Interface
BT interface Standard 5.0 is also available via the same SMA socket as for the WLAN interface.
▷ Log in to the RevPi via a terminal.
▷ Activate the HCI interface with the command:sudo systemctl enable hciuart
▷ Start the hciuart service with the command:sudo systemctl start hciuart
▷ Start the BT daemon with:sudo systemctl start bluetooth
See also:
USB Interfaces
The RevPi has two USB-A Interfaces. This allows USB 2.0 client devices such as USB hard disks, surf sticks, keyboards or mice to be connected. Both sockets together may be loaded with 1 A. How the current is distributed to both sockets is irrelevant. Z. For example, one socket can be loaded with 1 A and the other cannot be used. Or one socket is loaded with 300 mA and the other with 700 mA. For both connections together, 1 A must not be exceeded. If more than two USB-A ports are required, a USB hub can be connected.
LEDs
LED PWR
The PWR (Power) LED indicates the device status.
| Signal | Function |
|---|---|
| Green | Power supply is connected. |
| Red | There is a communication fault between connected modules. |
LED A1 – A5
LEDs A1 to A5 are customizable.
The LEDs can be used for user-specific requirements such as indicating a network connection, indicating that a memory limit has been exceeded, monitoring a process and indicating faults.
The LEDs can be switched in the command line application piTest with the variable RevPiLED.
The RevPiLED output has a defined byte length and therefore has a certain number of bits that are read from right to left. Certain bit positions are each assigned to an LED. The LED is switched by setting the respective bits to 0 or 1.
| LED | Assigned bit position |
|---|---|
| A1 | 0 to 2 |
| A2 | 3 to 5 |
| A3 | 6 to 8 |
| A4 | 9 to 11 |
| A5 | 12 to 15 |
An LED signal is set in the command line with the command piTest -w RevPiLED,x where x corresponds to the decimal value calculated from the respective bit pattern.
| LED | Signal | Bit pattern | Decimal value |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 – A5 | off | 0000 0000 0000 0000 | 0 |
| A1 | red | 0000 0000 0000 0001 | 1 |
| green | 0000 0000 0000 0010 | 2 | |
| blue | 0000 0000 0000 0100 | 4 | |
| orange | 0000 0000 0000 0011 | 3 | |
| cyan | 0000 0000 0000 0110 | 6 | |
| magenta | 0000 0000 0000 0101 | 5 | |
| white | 0000 0000 0000 0111 | 7 | |
| A2 | red | 0000 0000 0000 1000 | 8 |
| green | 0000 0000 0001 0000 | 16 | |
| blue | 0000 0000 0010 0000 | 32 | |
| orange | 0000 0000 0001 1000 | 24 | |
| cyan | 0000 0000 0011 0000 | 48 | |
| magenta | 0000 0000 0010 1000 | 40 | |
| white | 0000 0000 0011 1000 | 56 | |
| A3 | red | 0000 0000 0100 0000 | 64 |
| green | 0000 0000 1000 0000 | 128 | |
| blue | 0000 0001 0000 0000 | 256 | |
| orange | 0000 0000 1100 0000 | 192 | |
| cyan | 0000 0001 1000 0000 | 384 | |
| magenta | 0000 0001 0100 0000 | 320 | |
| white | 0000 0001 1100 0000 | 448 | |
| A4 | red | 0000 0010 0000 0000 | 512 |
| green | 0000 0100 0000 0000 | 1024 | |
| blue | 0000 1000 0000 0000 | 2048 | |
| orange | 0000 0110 0000 0000 | 1536 | |
| cyan | 0000 1100 0000 0000 | 3072 | |
| magenta | 0000 1010 0000 0000 | 2560 | |
| white | 0000 1110 0000 0000 | 3584 | |
| A5 | red | 0001 0000 0000 0000 | 4096 |
| green | 0010 0000 0000 0000 | 8192 | |
| blue | 0100 0000 0000 0000 | 16 384 | |
| orange | 0011 0000 0000 0000 | 12 288 | |
| cyan | 0110 0000 0000 0000 | 24 576 | |
| magenta | 0101 0000 0000 0000 | 20 480 | |
| white | 0111 0000 0000 0000 | 28 672 |
To switch several LEDs simultaneously, the respective decimal values have to be added up.
Example: If LED A1 shall flash red and LED A2 green at the same time, the command is piTest -w RevPiLED,17 (bit pattern: 0001 0001 = decimal values 1+16).
If a signal is to be added to an existing LED circuit, the value for all required signals must be recalculated and rewritten.
Watchdog
A watchdog is a timer that restarts the RevPi after 60 seconds. To prevent this from happening, the watchdog must be reset regularly as long as the system is running without errors. In the event of an error, such as a crash of the application process, there is no reset and the watchdog triggers a restart of the RevPi.
The RevPi has two independent watchdogs. There are several ways to use a watchdog under Linux. The RevPi image and Raspbian rely on systemd.
Integrated Watchdog
The watchdog integrated on the processor behaves like other watchdogs under Linux and can be addressed with:
/dev/watchdog0/dev/watchdog(as standard watchdog)
External Watchdog
A second watchdog is available via the RTC module and can be addressed under Linux with:
/dev/watchdog1
See also:
Relay output
The RevPi has a relay output on the lower X2 connector. This relay output can be used, for example, to interrupt the power supply to connected hardware.
- The relay can switch a maximum of 30 V and 300 mA.
- The relay contact is open after the start.
▷ Make sure that all devices are disconnected from their respective power supplies.
▷ Connect the load to be switched to the OUT pins on the X2 connector.
▷ Connect the power supply.
The relay output is defined in the process image via the status byte RevPiOutput, Bit 0.
Digital input
The RevPi has a digital input for a +24 V input signal on the lower X2 connector. The input has an internal pull-down resistor.
The digital input can be used to connect a UPS.
▷ Make sure that all devices are disconnected from their respective power supplies.
▷ Connect the signal transmitter to the IN+ and IN- pins of the X2 connector.
▷ Connect the power supply.